web3 wallets as documentation wallets. The simplicity of the «Connect Wallet». The Proof of Humanity protocol, UBI and its idea of a universal basic income.
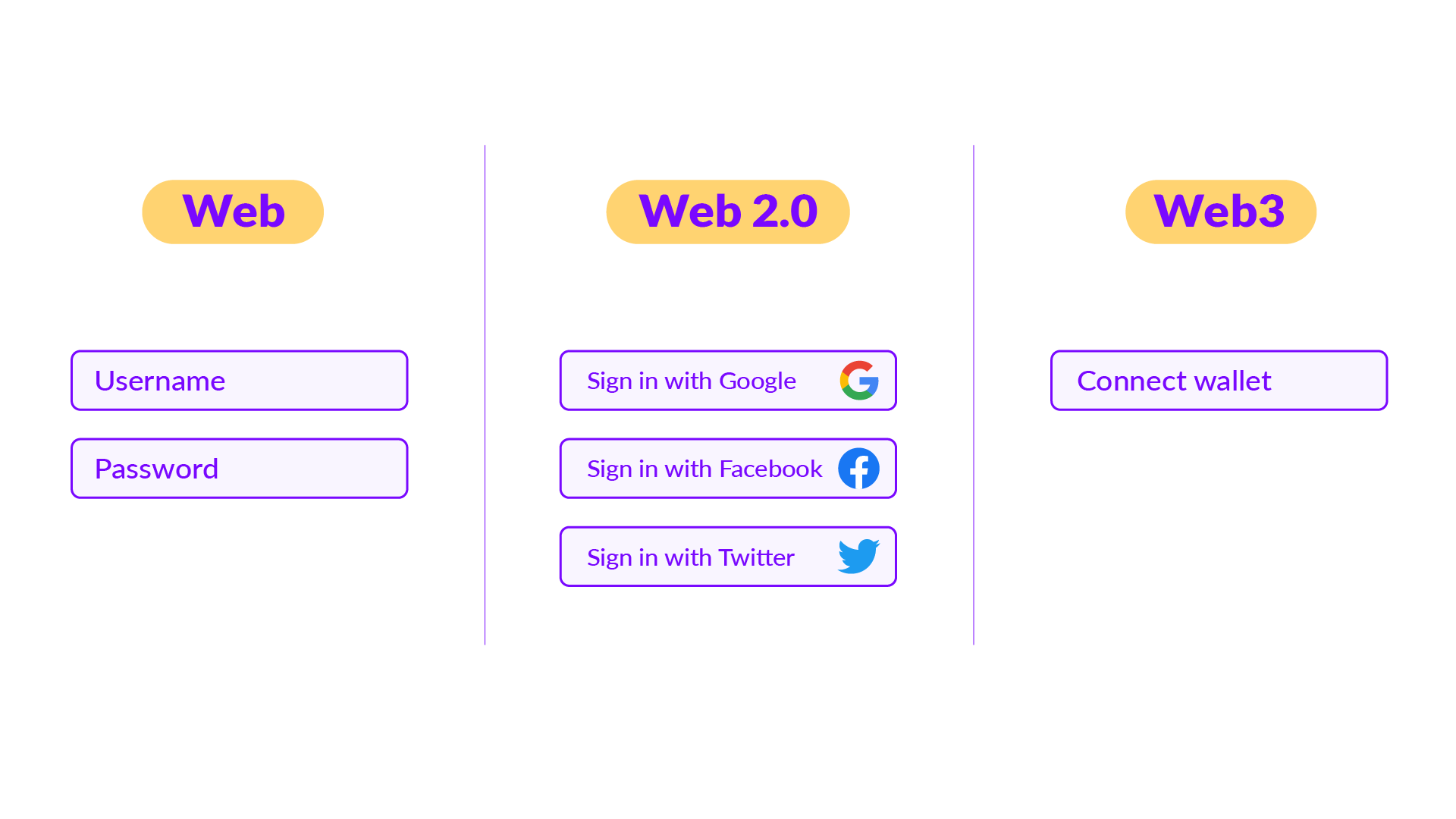
Web3 not only brought new applications in the form of dapps, but also its own ways of interacting with them. One of the easiest changes to notice is in the account and login system.
On the first website you needed an email, a password and filling out forms with a lot of personal information.
In web 2.0, having an account on a mainstream platform such as Google or Facebook (Meta) already in some way «validates» a person’s identity, and allows them to log in to sites of all kinds.
On web3, just connect a wallet to use a dapp.
These decentralized wallets for managing cryptocurrencies, such as Ripio Portal for example, are essential for web3, because they manage crypto addresses, which function as a kind of master key or credential that allows access to services.
These crypto addresses are what allow dapps to recognize a user’s «history» without demanding information from them: their collection of tokens or NFTs, their funds loaded on the platform, their tokens available to perform actions, even their settings.
These wallets can be used independently, like any traditional app, or integrated into browsers for a more seamless web experience3. There are even browsers designed especially for exploring the web3, like Brave.
UBI and the Proof of Humanity
Proof of Humanity is a consensus protocol that allows validating the real existence of people, and digitally identifying them in a blockchain context. Establishing robust and secure methods to validate identity is essential on the web3, especially in voting and governance systems.
Unlike state documents, which are generally falsifiable, or the private systems of web 2.0 platforms, the Proof of Humanity model offers a decentralized, transparent and attack-resistant digital identification system.
To each person who «validates their humanity» with PoH, the project constantly and permanently delivers an amount of the Universal Basic Income (UBI) token, which as the name suggests is intended to constitute a «universal basic income.»
What is decentralized finance? Advantages of DeFi over traditional finance. What to do in DeFi. Key concepts: dexes, lending, pools, staking.

What can be done in DeFi
Just like in regular finance, with DeFi you can “deposit” crypto to generate a return, or “borrow” tokens. Cryptocurrencies can also be exchanged in an automated way, without the need for intermediaries, with simple and friendly interfaces.
The key piece of DeFi is decentralized exchanges or dexes, which allow tokens to be exchanged in an automated manner. This is very important in DeFi, where the profit offering of one protocol or another can change frequently and it is important to be able to obtain liquidity for the tokens with the best return or performance, as quickly as possible.
The most common movements in the decentralized finance ecosystem are lending and borrowing: literally, lending and borrowing a certain amount of cryptocurrencies or tokens.
One of the possibilities is to contribute cryptocurrencies to a liquidity pool, to a «pool» where other crypto users also dump theirs. In exchange, you obtain a token that represents that amount, and an extra return when the pool «moves»: when there are people who operate with those tokens and pay commissions.
On the other hand, when someone needs to borrow a certain amount of a token or cryptocurrency, they can request it in an automated manner and offer collateral, a deposit of equivalent value that is repaid when the loan is returned and serves as insurance for the operation.
Another particular type of deposit is staking, which consists of locking a certain amount of a token in exchange for a return, in a similar way to how fixed terms work for the user. Funds can be «left there», generating returns, or withdrawn at any time.
Characteristics of non-fungible tokens. Use of NFTs in the web3, the metaverse and blockchain video games. Marketplaces: the stores where NFTs are purchased.


NFTs are a type of tokens called non-fungible, which represent unique digital assets and whose main usefulness is that they allow you to assign ownership, identify and differentiate all types of data packages registered in the blockchain: such as land or the property of a company, but also as songs, images or video game characters. Therefore, in the crypto community, the importance of NFTs is not only economic, but above all cultural.
Unlike cryptocurrencies, which are equivalent and substitutable tokens (that is, fungible), non-fungible tokens are unique, well differentiated and identified, and even though two have the same value and the same appearance, they are different in their content and cannot be replaced.
A painting, for example, is non-fungible: no two are alike, even making an exact replica will not be the same painting as the original, nor will it be worth the same nor will it have the same symbolic weight. NFT art or crypto art adds an extra layer of immutable information about the originality and uniqueness of a work, thereby also ensuring rights for its creator and owners.
NFTs also sneak into entertainment: not only as collectibles or as an area of striking interest due to the graphic appearance that most have, for example, but also in the form of video game characters or items that allow players to feel part of the game. of that world but also get a reward or performance for your hours of play, your skill or your creativity.
On the other hand, NFTs are essential to the metaverse. In this digital environment strongly connected to cryptocurrencies and tokenized economies, NFTs can serve many purposes. NFT crypto art can be displayed in the metaverse, but there are also NFTs that can be used as avatars or characters or mascots, and there are also many metaverse projects that sell digital land under the NFT format.
Decentralized autonomous organizations on the web3. Governance, participation, investments and collective properties. On chain versus off chain deliberation.

DAOs also accept donations or can engage in collective trading and investment. And how do you reach an agreement on what and how to use those funds? Through voting that can also be carried out without any intermediary body.
In short, a DAO is an organization of people who come together around an interest or mission. DAOs are funded with crypto and coordinate their actions through a set of transparent rules written as computer code in a smart contract, and published and secured on a blockchain. This makes them work in a transparent and distributed way.
On the other hand, the projects, platforms and protocols of the crypto ecosystem can be managed on chain or off chain, concepts that sometimes coincide with decentralized and centralized models. That is, on chain is the type of governance that occurs through the mechanisms of the blockchain itself, such as governance tokens and smart contracts, and that most often operate in a decentralized manner. DAOs, by definition, are run this way. While off chain is the traditional model where a person or a small group manages the threads of the project in a discretionary manner.



